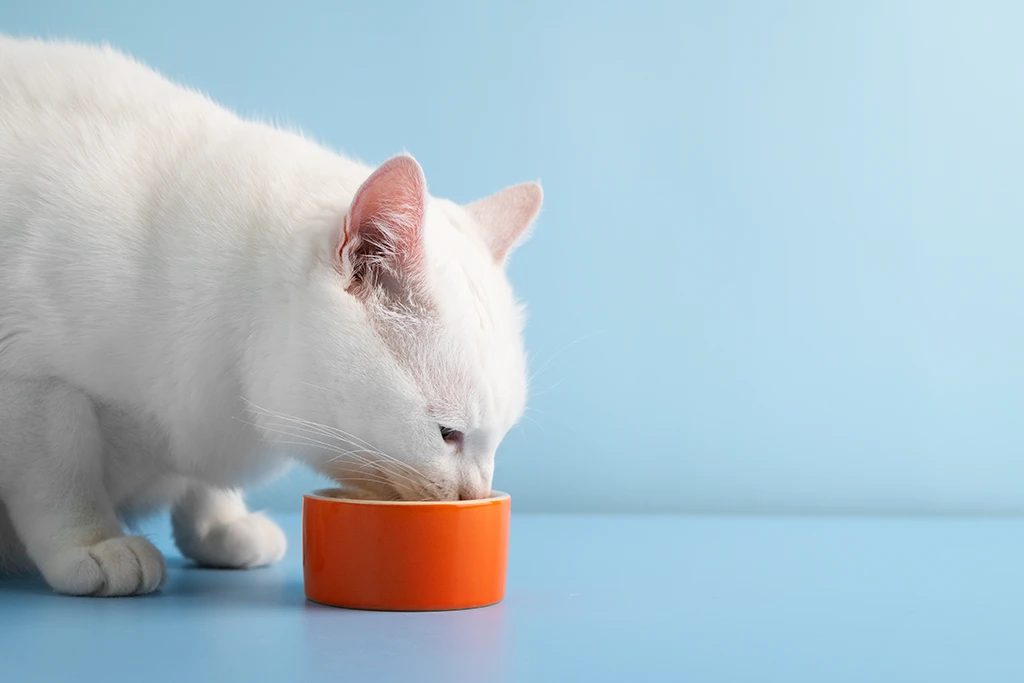
Watching a beloved buddy turn their nose up at their favorite food is a frustrating and upsetting experience. Veterinarians often hear concerns from pet parents about their dog or cat’s sudden lack of interest in mealtime. Although there are numerous causes of decreased hunger, CBD oil is becoming more popular as a possible remedy. But does CBD really stimulate a pet’s appetite? Let’s dig in!
Table of Contents
ToggleIt’s dinnertime, and a furry friend is nowhere to be found. Even worse, they get a whiff of their meal and then disappear. It is worrying when a pet suddenly shows disinterest in food. Before diving into details on how CBD helps, explore some common culprits behind appetite loss in pets.
A pet’s lack of appetite might occasionally be an indication of a more serious health problem. Dental problems, like a sore tooth or gum disease, make chewing painful. Infections, whether bacterial or viral, cause nausea and discomfort, making food unappealing. Organ dysfunction, such as kidney or liver disease, also affects appetite.
The appetite of pets can be affected by side effects of several medications, even if these medications are vital for treating many illnesses. Some medications cause nausea or vomiting, while others alter taste perception, making food seem less appealing. If a pet’s medication is affecting their appetite, talk to the pet’s veterinarian about potential alternatives or ways to manage the side effects.
Animals get anxious and stressed out much like people. An individual may experience these emotions in response to changes in their daily routine, relocation, the arrival of a new family member or pet, or the loss of a loved one. Stress and anxiety frequently cause a decrease in appetite.
If a pet suddenly stops eating a specific food they once enjoyed, they possibly develop a food sensitivity or allergy. Common culprits include beef, chicken, dairy, and wheat. Identifying and eliminating the offending ingredient from their diet helps restore their appetite.
As pets enter their golden years, their senses of taste and smell decline, making food less enticing. Declining digestive function or cognitive impairment are only two examples of the age-related health problems that impact their hunger.
If a pet is showing signs of appetite loss, it’s important to consult the pet’s veterinarian to rule out any underlying medical conditions and determine the best course of action.

While a missed meal here and there is not a big deal, persistent changes in a pet’s eating habits warrant attention. But how to tell if a pet’s appetite loss is something to worry about? Some key signs and symptoms to watch for are listed below.
The most obvious sign of appetite loss is a decrease in the amount of food a pet consumes. They refuse to eat at all, consume less than they usually do, or pick at their meals. If a pet consistently leaves food in their bowl or shows no interest in treats they once loved, it’s time to investigate further.
Consistent appetite reduction frequently results in appreciable weight loss. This is particularly concerning in smaller pets or those with existing health conditions. Regularly weighing pets and monitoring their body condition helps pet owners detect weight loss early on.
If a pet seems less active and playful than usual, it is a potential sign of an underlying issue affecting their appetite. Lethargy, or a lack of energy, accompanies various medical conditions and indicates that a pet isn’t feeling well.
Pet behavior changes indicate an issue. They become more withdrawn or hide more often. Some pets exhibit increased aggression or irritability, while others vocalize more frequently. These behavioral changes, coupled with appetite loss, indicate an underlying health issue or emotional distress.
Schedule a visit with the pet’s veterinarian if any of these signs are observed. They help determine the cause of the appetite loss and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Following the discussion of the reasons pets may be picky eaters, it is now time to look at how CBD might help get them to return to their food bowl. CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) of the companion, a complex network of receptors that aids in the maintenance of body equilibrium, as previously mentioned. Appetite and digestion are two of the many processes that benefit from this connection.
Consider the ECS as the internal balancing act of a pet making sure everything from mood and sleep to hunger and immune system is in sync. CBD influences this system, promoting overall well-being and potentially addressing specific issues that contribute to appetite loss.

Now that we know, How CBD may help with your furry friend’s appetite. Take a closer look at how CBD benefits a pet’s appetite below:
Anxiety and stress significantly suppress a pet’s appetite. Imagine feeling so worried to the point of not even thinking about food, hence missing meals! A pet’s anxiety about eating can be alleviated with cannabidiol (CBD). A calmer mind often leads to a relaxed and enjoyable eating experience.
Nausea and vomiting are surefire appetite killers. If a pet feels queasy, the last thing they want to do is eat. CBD may help reduce these symptoms, making a pet more comfortable and increasing the likelihood that they are going to eat.
Digestive discomfort also contributes to appetite loss. Inflammation in the digestive tract produces pain and discomfort, which makes eating uncomfortable. And, CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties may help soothe the gut and promote healthy digestion, making mealtime more enjoyable for a pet.
Sometimes, appetite loss stems from an underlying inflammatory condition. CBD may alleviate inflammation and increase pet appetite. Also, CBD may help restore their appetite and general well-being by addressing the underlying source of their suffering.
CBD’s potential benefits extend beyond addressing specific symptoms. By promoting a sense of calm and relaxation, CBD may contribute to a pet’s overall well-being. An improved quality of life for a pet increases the likelihood that they will eat healthily and savour their meals.
It’s important to note that while CBD shows promise in stimulating appetite, it’s not a magic cure-all. It’s essential to work closely with the pet’s veterinarian to determine if CBD is right for the pet and to address any underlying health conditions contributing to their appetite loss.
The perfect CBD product for a furry friend is now established. Now, how to get that beneficial CBD into their system? Don’t worry, it’s often easier than most think! Know the different methods of administering CBD to pets as discussed below.
Oral administration is the most common and often most effective way to give a pet CBD, especially when the goal is appetite stimulation. There are a couple of ways to go about it.
Adding CBD oil to food: This is a fantastic option for pets who are enthusiastic eaters. Simply add the recommended dosage of CBD oil to the pet’s food and mix well. Their meal’s taste usually hides the taste of the oil, so it’s easy to provide CBD.
Direct administration with a dropper: For pets who are a bit more discerning about their food or require a precise dose, administer CBD oil directly into their mouth using a dropper. Place the oil on their gums or under their tongue after gently lifting their lip and placing it there. This allows for quicker absorption into the bloodstream.
CBD treats are a popular choice for pet parents seeking a convenient and palatable way to administer CBD. With the added advantages of CBD, these treats are just as delicious as any other pet treat. They’re pre-measured, making dosing a breeze, and most pets gobble them up without a fuss.
Topical CBD products, such as balms and creams, are typically used for localized relief. Think of it like applying a soothing ointment to a sore muscle. While topical CBD provides overall benefits, it’s not the primary method for stimulating appetite. However, if a pet enjoys a gentle massage, applying a CBD topical is a relaxing and enjoyable experience for both parents and pets!
It is important to begin with a modest dose and raise it gradually as needed, regardless of the method chosen. Always monitor a pet for any changes in behavior or appetite, and consult a veterinarian if there are any concerns.
Although cannabidiol (CBD) is a useful tool, it is essential to seek the advice of a veterinarian before beginning any new supplement for a pet. This is especially important if the pet is already receiving drugs or has preexisting health conditions.
CBD shows promise as a natural way to help a pet eat, especially when worry, stress, or sickness are making them lose their appetite. By understanding how CBD works, choosing the right product, and working closely with a veterinarian, pet parents help a furry friend regain their zest for mealtime.
Never forget that your pet is an individual, and it may take some trial and error to discover what works best for them. But with patience, observation, and a little help from CBD, pet parents help a pet enjoy their food and thrive!
References

Table of Contents
Toggle